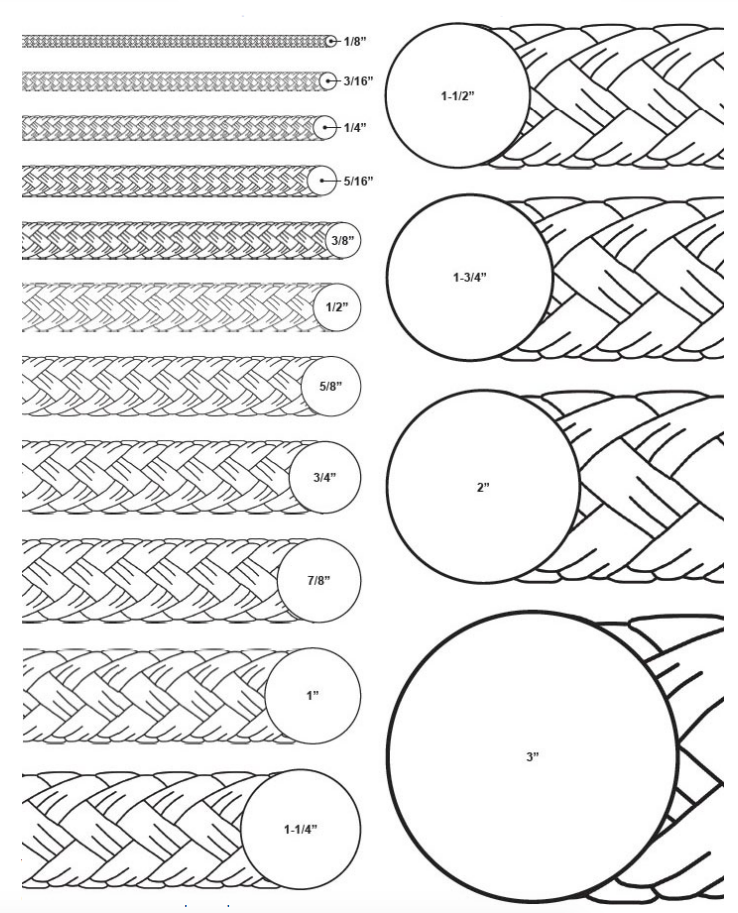
Synthetic Fiber Rope Definition

Ci 1302a ci 1302b rope fiber.
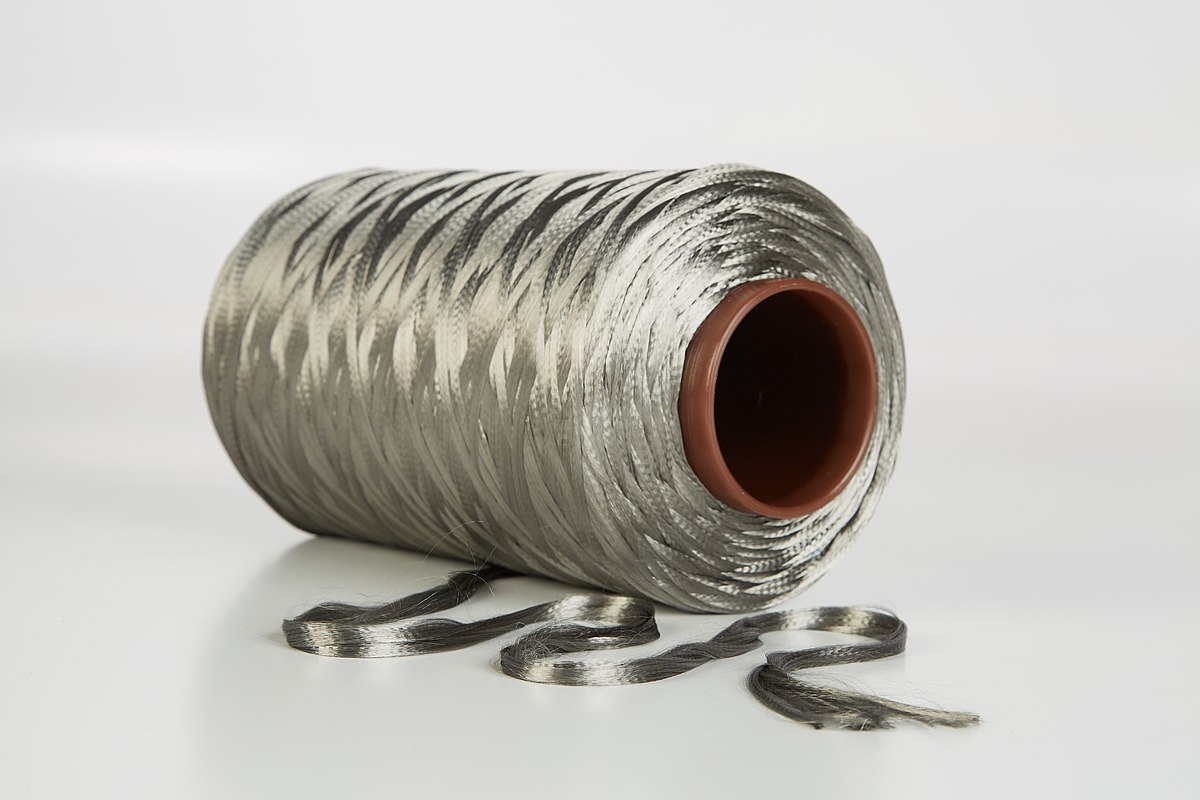
Synthetic fiber rope definition. The first synthetic fiber rope manufactured. Synthetic rope is lightweight and has a 20 percent stronger tensile strength than natural fiber ropes. Synthetic rope does not shrink when wet like natural fiber ropes. A compact but flexible torsionally balanced structure produced from strands which are laid plaited or braided together to produce a product which serves to transmit a tensile force between two points.
It has very good resistance to abrasion and will last four to five times longer than natural fiber ropes. The load a rope is rated to handle assumes that the load is static and not moving. As hmpe fibers have a low friction coefficient and good abrasion resistance the results are comparable with those from commonly used synthetic fiber ropes like polyester or nylon and far higher than other high tenacity fibers like aramids and carbon fibers. Mooring fiber ropes can experience various types of damage as discussed below.
Ropes never return to their original length once creep sets in. Creep is the amount synthetic fibers slowly stretch while handling a continuous load. Dynamic or moving loads greatly reduce the ability of a rope to hold the load. Unlike synthetic rope however the natural rope isn t damaged by exposure to high heat and will only burn if exposed to actual flames.
See spelling differences are fibers made by humans through chemical synthesis as opposed to natural fibers that are directly derived from living organisms. For an installed fiber mooring line damage can also be caused by a falling object or contact with. Due to its elasticity nylon can absorb sudden shock loads that would break ropes of other fibers. They are the result of extensive research by scientists to improve upon naturally occurring animal and plant fibers in general synthetic fibers are created by extruding fiber.
Synthetic fibre ropes are significantly stronger than their natural fibre counterparts they have a higher tensile strength they are more resistant to rotting than ropes created from natural fibers and they can be made to float on water. Unfortunately natural rope tends to shrink when it gets wet and can be very difficult to work with once it has been gotten wet and then dried again. It will melt though when exposed to heat unlike natural fiber ropes that are damaged only by direct contact with fire. Nylon rope is rot proof and not damaged by oils gasoline grease marine growth or most.
12 4 3 inspection of fiber rope. Rope fibers and strands move relative to each other and cause internal abrasion. Synthetic fiber or synthetic fibre in british english. Cut or abrasion fiber rope damage is often caused by contact of the fiber rope with sharp edges during rope deployment or retrieval.